Small-sized boats. Types of small-sized boats. Basic definitions
A boat is an engineering structure capable of moving on water and carrying loads and people. Thus, the boat will be both a kayak and an ocean liner. Boats built for military purposes and part of the Navy are commonly called ships.
Small-sized boats are used for hiking and walking, fishing and hunting, sports, etc. They are widely used for the needs of the national economy. In many areas (especially in Siberia), small boats are the main means of transport for individual use during navigation.
On all rowing boats, both on-board and outboard or stationary outboard motors can be used (with the exception of only academic rowing boats). On sailing yachts, it may be necessary to move under the motor. Rowing and sailing boats, when using a motor, are subject to all the rules relating to boats with mechanical engines.
The modes of movement of small motor boats are different: these are displacement and planing boats, hydrofoil boats and air cushion.
Displacement boats (Fig. 1) are always kept afloat only due to the Archimedean «support force» equal to the mass of water displaced by the boat.
Displacement boats, although they have the greatest seaworthiness compared to other boats, their speed is much lower than the latter.
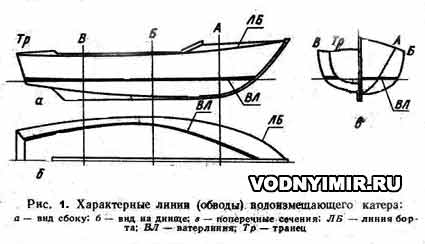
Planing boats (Fig. 2) are kept afloat in a stationary state due to the same «maintenance force» as displacement boats. With an increase in speed, planing boats are supported on the water already due to dynamic lifting forces arising on flat sections of the bottom. The planing boat starts planing when its flat bottom is located at an angle of attack to the water surface in 3-6 degrees at a certain minimum speed, depending on the total weight of the boat with equipment, motor and passengers.
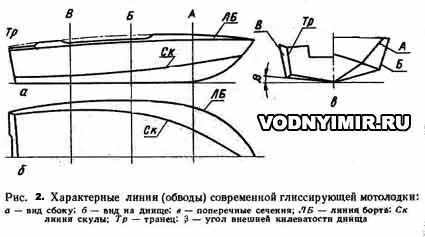
To motor boats (motor boats) includes all commercially available pleasure boats with outboard motors. Motor boats are also called homemade boats with low-power stationary boat engines operated in displacement mode of movement. Such boats of local construction, unlike planing ones, have relatively smooth contours.
Boats are small boats with a stationary engine. Service boats can be built for operation in planing and displacement modes of movement. Boats of increased seaworthiness have a deck, cockpit, superstructure.
Seaworthy motor boats and boats with a length of usually 6-8 m with boat (displacement) contours, designed for navigation in open water spaces and in the mouths of large rivers, are called bots or motor bots and various local names.
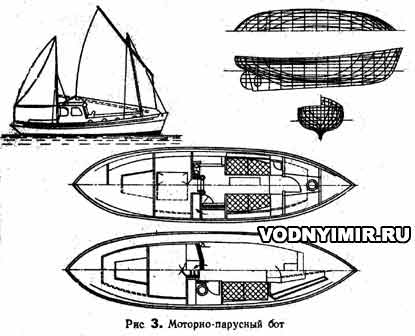 Bots usually have an add-on and a stationary engine. Bots having both an engine and sailing armament are called motor-sailing bots (Fig. 3). Bots are divided depending on the tasks they perform into pilotage, fishing, rescue, diving, etc.
Bots usually have an add-on and a stationary engine. Bots having both an engine and sailing armament are called motor-sailing bots (Fig. 3). Bots are divided depending on the tasks they perform into pilotage, fishing, rescue, diving, etc.
Boats include all rowing and motor small boats, which are regular watercraft of ships and boats of all types of the fleet. They serve to rescue people, transport (communication with the shore and other vessels, etc.) and special (delivery of anchors, outboard and other work) purposes. Therefore, the boats are called — rescue, workers, etc.
Yachts are, first of all, sailing, as well as motor, motor-sailing boats of various displacement, designed for recreation on the water, tourism and sports. Hence the motor yacht, motor-sailing and just sailing.
A skimmer is a motor boat that has redans — transverse ledges on the bottom (more often one, less often several). Single-seat racing gliders with outboard motors are called scooters. If a small boat has hydrofoils to increase its speed, then it is usually called a boat (motor boat) on hydrofoils.
In the section «Motorboats, boats, yachts — miscellaneous, reviews, tips»
Share this page in the social. networks or bookmark:
