Project and drawings of a seaworthy motor boat — motorboat for large reservoirs

When developing the design and drawings of this motor boat, I counted on the fact that anyone could build it who has little skills with carpentry tools. Also, the boat was intended for sea bays and large reservoirs, so it had to have increased seaworthiness — the ability to go through the waves, not reducing the speed, while not splashing and not being flooded with high wave crests.
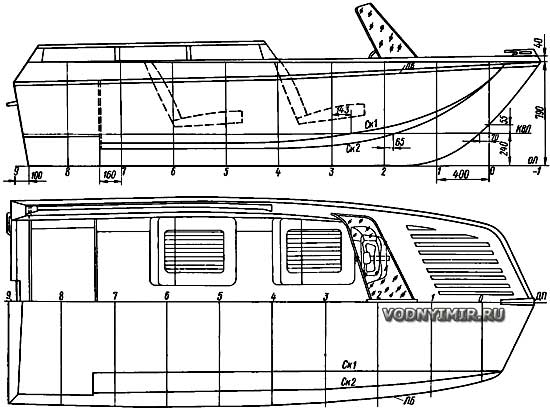
General view of a motor boat for large reservoirs
Water particles in the wave profile make a rotational motion in circular orbits, and at the crest the direction of their movement coincides with the direction of the waves. On the sole of the wave, water particles move in the opposite direction. For this reason, hydrodynamic forces are acting on the boat that has risen sideways to the wave, striving to turn it over. These forces are combined with buoyancy forces, with wind pressure on the hull and superstructure, and with inertia forces if the boat was moving at a good speed up to this point. As a result, a boat with a sharp nose can capsize, often unexpectedly for its driver and passengers. Once in the middle of the reservoir, those in trouble do not have to rely on an ambulance in fresh weather, and the crew of the boat is doomed to fight for salvation on their own.
Everyone who went by boat in a large reservoir felt that the swimming conditions here are more difficult than on the river. A sharp nose often sticks into a wave, water floods the deck. And it is only necessary to reduce the stroke, as a full wide stern pops up, and the nose drops even lower. On a passing wave, a boat with traditional contours, catching up with the wave, enters it with a narrow nose and slows down. The next wave lifts the full wide stern, the bow begins to literally «plow» the water, which can even roll out onto the deck and flood the boat. If the helmsman makes a mistake at the same time, does not hold the boat in time, then the crest of the wave can throw the stern to the side — turn the boat around the nose «stuck» in the water. The boat becomes a side to the wave.
The proposed design of a three-keel motorboat is devoid of the mentioned disadvantages. The nose of the motorboat is wide, there are side extensions on the hull — additional volumes of buoyancy that prevent a large roll. Maintaining stability on the roll is facilitated by a large (up to 18°) keeling of the bottom. It also softens the blows of the hull of the boat on the waves, makes swimming more comfortable. The large keel extends to the transom, so the stern does not float up on the wave as sharply as in a flat-bottomed boat. Having tested this boat in the Gulf of Finland, I was convinced that it easily goes through the wave both at full and at low speed. The wave sometimes reached 2.5 meters in height!
Theoretical drawing of a motor boat
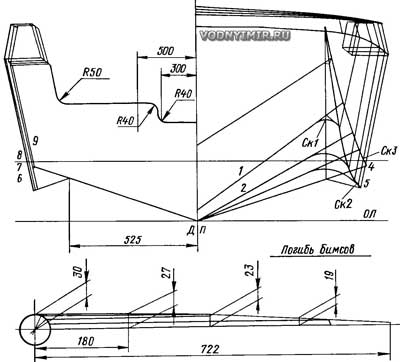
Table of plaz ordinates, mm
| Lines | frame no. | |||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| Heights from OL, mm | ||||||||||
| Board LB | 754 | 732 | 713 | 700 | 682 | 670 | 660 | 645 | 639 | 635 |
| Cheekbone I — Sk. 1 | 642 | 410 | 292 | 220 | 185 | 176 | 176 | 176 | — | — |
| II — Sk. 2 | 645 | 385 | 224 | 160 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | — | — |
| III — Sk.3 | 650 | 485 | 350 | 285 | 245 | 230 | 230 | 230 | — | — |
| Half-width from DP, mm | ||||||||||
| lb | 606 | 670 | 722 | 759 | 780 | 790 | 795 | 790 | 775 | 750 |
| Sk. 2 | 542 | 585 | 630 | 650 | 667 | 679 | 680 | 679 | — | — |
| Sk. 3 | 560 | 600 | 645 | 660 | 680 | 690 | 680 | 673 | 666 | 660 |
The hull of the boat can be made of a wooden structure with a plywood skin, as shown in the drawings. Some amateur shipbuilders used fiberglass for sheathing, they also built this boat with a set of metal square with duralumin sheathing, riveted construction.
Cross sections no frames
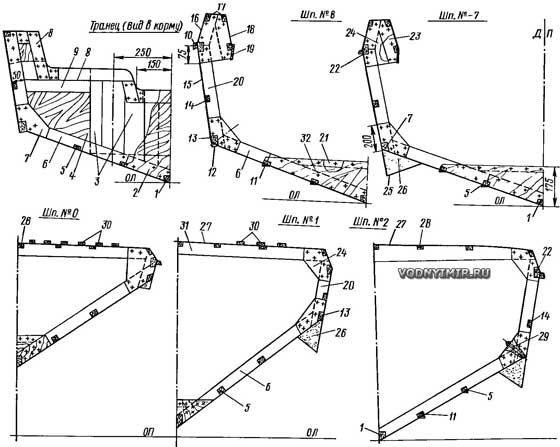
1 — keel, 30x60; 2 — internal transom stitching, δ=6; 3 — placeholder, δ=20; 4 — transom, δ=8-10; 5 — bottom stringer, 15x30; 6 — flortimbers, 20x50; 7 — zygomatic knits, δ=4-6; 8 — transom strapping, 20x50; 9 — duck cushion, 20x60; 10 — collar, 20x15; 11 — longitudinal redan, 15x30; 12 — zygomatic mudguard, 15x30; 13 — zygomatic stringer, 30x40; 14 — side stringer, 15x30; 15 — side skin, δ=4; 16, 18 — bulwark, δ=4; 17 — rail, 20x20; 19 — coaming, 8x50; 20 — toptimbers, 20x50; 21 — rail, 20x25; 22 — privalny beam, 25x40; 23 — half-beams, 20x50; 24 — knits, δ=4; 25 — pasting of the sponsor with fiberglass; 26 — foam; 27 — deck flooring, δ=5; 28 — deck stringer, 15x30; 29 — bolt M6x100; 30 — decorative slats, 8x30; 31 — beams, 20x50; 32 — flor, plywood δ=4.
In the manufacture of motor boats made of wood, the parts are assembled using water-resistant glue. The outer surface of the plywood covering is recommended to be thoroughly sanded and pasted with one or two layers of fiberglass on an epoxy or polyester binder. The thickness of the plywood outer skin on the bottom and deck is 5 mm, on the sides — 4 mm. The technological processes of manufacturing parts and assembling the hull are described in detail in the book «15 projects of vessels for amateur construction», 1985, L-d, «Shipbuilding».
It is best to paint a motor boat with epoxy enamels, but pentaphthalic enamels can also be used.
In the transom, it is necessary to fix the sleeve with a threaded plug, which is unscrewed on the shore to drain the water that has entered the housing.
It is necessary to operate the motor boat only with remote control motors. When going out in fresh weather, the crew is obliged to wear life jackets, necessarily with a solid foam filler.
Boat projects for self-construction
Share this page in the social. networks or bookmark:
